Every Scorbase project includes a set of pre-defined positions and a program that sends the robot from one position to another. Prior to running a program, all the positions used in that program should be defined. Scorbase offers various tools to define and store positions that will be used in the programs.
- Manual movement dialog box
- Teach position dialog box
- Robot movement dialog box
- Positions Window
To activate the dialog boxes which are most useful for position definition, select Window|Teach & Edit
Any of the following methods can be used for position definition:
- Cartesian coordinates: A robot position in Cartesian (or XYZ) coordinates is defined by these parameters. The distance of the robot’s Tool Center Point (TCP) from the point of origin (the center bottom of the robot base), along the three axes that describe three-dimensional space (X,Y,Z). The Pitch (P) and Roll (R) angles of the gripper, specified in angular units.
- Joint coordinates: A robot position in Joint coordinates is defined by five angle values for the ER 9Pro robot, representing each angle of the joints.
- The joint names are Base
 , Body, Upper Arm, Forearm, and Flange.
, Body, Upper Arm, Forearm, and Flange.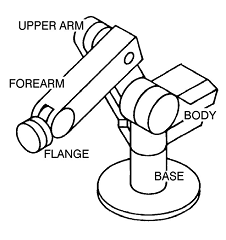
- Absolute position: An absolute position is defined using all five robot position parameters. If the Joint coordinate system is used, the robot position is defined using the Base, Shoulder, Elbow, Pitch, and Roll angles. In the XYZ coordinate system, a position is defined using the X, Y, Z values in millimeters, and the Pitch and Roll angles in degrees. An absolute position is usually a fixed position in world space.
- Relative position: A relative position is a position whose coordinates are defined as an offset from a reference position coordinates. If the coordinates of the reference position change, the relative position moves along with it, maintaining the same offset. A relative position can be defined in either Cartesian or Joint coordinate values. A position can also be defined as relative to current. In this case, the relative position is calculated as an offset from the coordinates of the current robot position.