Theory
Ultrasonics Thickness Measurement
Ultrasonics thickness measurement is a method of performing non-destructive measurement of the local thickness of a solid element (typically made of metal) basing on the time taken by the ultrasound wave to return to the surface. This type of measurement is typically performed with an ultrasonics thickness gauge.
Use of ultrasonics wave for fault detection

Ultrasonics waves are sent through the material under consideration and the beam reflected from the other end of the material. The time of travelling of a beam can be noted and is referred to as transit time t. The application of transit time is to measure the wall thickness. The measured wall thickness is being multiplied by the sound velocity of the material and half of this will be the thickness of the material.
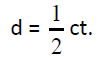
where,
d is the thickness of material.
t is the transit time of wave.
c is the velocity which is assumed to be constant for a given material.
Advantages of using Ultrasonics
1. High penetrating power, which allows the detection of flaws deep in the part.
2. High sensitivity, permitting the detection of extremely small flaws.
3. Only one surface need be accessible
4. Greater accuracy than other nondestructive methods in determining the depth of internal flaws and the thickness of parts with parallel surfaces.
5. Some capability of estimating the size, orientation, shape and nature of defects.
6. Nonhazardous to operations or to nearby personnel and has no effect on equipment and materials in the vicinity.
7. Capable of portable or highly automated operation.